






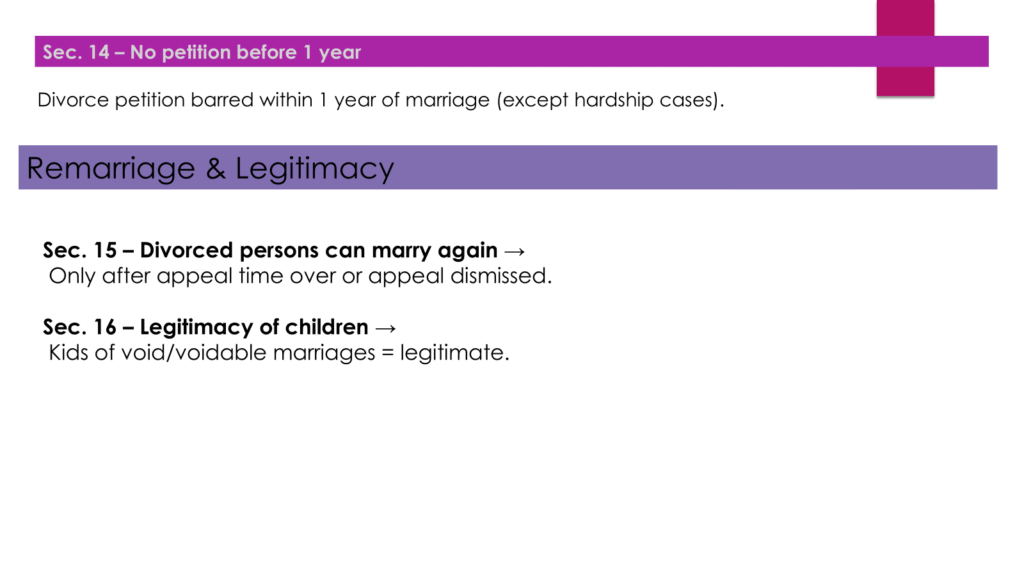
Sec 16 — Legitimacy of children (void / voidable marriages)
Children born of marriages that are later found void or voidable are still treated as legitimate.
Legitimacy protects the child’s legal rights (for inheritance from parents).
Idea: the law shields the child even if the marriage had defects.
Key Point: “Child’s status ≠ parents’ flaw.”
Sec 17 — Bigamy: legal consequence
Marrying while a living spouse exists → second marriage is void and may attract criminal liability (IPC).
Purpose: enforce monogamy among Hindus.
Note: bigamy can lead to penal action and nullity of the later marriage.
Key Point: “No second vows while first stands.”
Sec 18 — Penalty for flouting marriage rules
If essential conditions (like minimum age, consent, prohibited relationships) are ignored, there are penalties prescribed.
Punishments vary with the breach — may include fines or imprisonment.
Practical: safeguards basic safeguards for a lawful marriage.
Key Point: “Broke the rule → face the penalty.”
Sec 19 — Which court to approach
Matrimonial petitions go to the District Court (or other competent civil court) where:
the marriage took place, or
the couple last lived together, or
the respondent resides.
Aim: pick the convenient, proper forum for the case.
Key Point: “File where marriage lived.”
Sec 20 — What to put in the petition
Petition must state facts clearly: marriage details, grounds, relief sought, and be verified/signed.
Oaths and accurate statements required; false claims can be punished.
Tip: keep facts chronological and attach supporting documents.
Key Point: “Clear facts, signed truth.”
Sec 21 — Rules of civil procedure apply
Civil procedure rules (general court procedure) govern how petitions are handled.
Ensures a standard court process for matrimonial matters.
Key Point: “Matrimony follows civil procedure.”
Sec 21A — Transfer of petitions
If spouses file in different courts, cases can be transferred so one court decides both matters together.
Prevents conflicting orders and duplication.
Key Point: “Two courts → one court.”
Sec 21B — Special measures for speedy disposal
Courts are expected to speed up matrimonial trials and avoid unnecessary delay.
Purpose: reduce emotional and economic hardship caused by slow litigation.
Key Point: “Fast track family matters.”
Sec 21C — Documents as evidence
Documents (marriage certificate, letters, photos, medical or financial papers) are admissible and important.
Keep originals or certified copies to support your claim.
Key Point: “Paper proves what words cannot.”
Sec 22 — Private hearings (in camera)
Matrimonial proceedings are normally private; details shouldn’t be published.
Protects reputation and personal privacy of parties and children.
Key Point: “Closed doors, protected lives.”
Sec 23 — Court’s decree (final orders)
After hearing, the court issues its decree — it may confirm, annul, or dissolve the marriage, or pass other orders.
Decree is the authoritative outcome of the suit.
Key Point: “Hearing ends → decree writes the result.”
Sec 23A — Relief available to the respondent
The responding spouse can also seek relief or counter-claims — court hears both sides’ rights.
Ensures fairness and prevents one-sided justice.
Key Point: “Defence has its remedy too.”
Sec 24 — Interim maintenance & litigation costs
While case is pending, the financially weaker spouse may get temporary maintenance and help for legal expenses.
Keeps the dependent spouse afloat during proceedings.
Key Point: “Justice support while you wait.”
Sec 25 — Permanent maintenance / Alimony
On final decision, court may order long-term support (monthly or lump-sum) after considering income, needs, conduct, etc.
Can be adjusted if circumstances change.
Key Point: “End of marriage ≠ end of duty.”
Sec 26 — Child custody & welfare
Court decides custody primarily based on the welfare of children — care, education, and stability matter most.
Orders can be temporary or permanent, with visitation rules as needed.
Key Point: “Child’s well-being first.”
Sec 27 — Property: how it’s settled
Court can make orders about distribution / use of property acquired during marriage.
Factors: contributions, needs, fairness.
Key Point: “Shared life → fair share.”
Sec 28 — Right to appeal
Parties unhappy with a decree/order can appeal to a higher court within the prescribed time.
Appeals allow review and correction of errors.
Key Point: “If wrongly judged, ask again.”
Sec 28A — Enforcement of orders
Courts have power to enforce their decrees (for maintenance, custody, property recovery).
Ensures court orders are not just words.
Key Point: “Order given → order done.”
Sec 29 — Savings clause
Existing customs, laws, or special provisions continue unless they conflict with this Act.
Means the Act doesn’t automatically wipe out all prior rules.
Key Point: “Old rules stay—until they clash.”
Sec 30 — Repealed
This section has been removed and is no longer operative.
